Abstract
Aims
The objective of this study was to compare the performance of the novel Cepheid Prototype Xpert® NPM1 Mutation Assay to the Qiagen ipsogen® NPM1 mut A, B&D MutaQuant Kits using samples contrived using cell line-spiked peripheral blood. Our goal was to evaluate the comparative performance of a faster and easier to use assay than commercially available products for use in the monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD) in NPM1-positive AML patients.
Background
A common mutation in AML (20-30% of cases) is a four base pair insertion in the NPM1 gene.¹ NPM1 plays a role in ribosome biogenesis, maintaining genomic stability, and modulating growth suppression by binding and stabilizing p53.² NPM1 mutant A consists of about 80% of NPM1 mutations, while mutants B or D are present in a sizeable minority of patients.¹² Monitoring of NPM1 mutations can provide prognostic value and can assist with choice of treatment.³
Methods
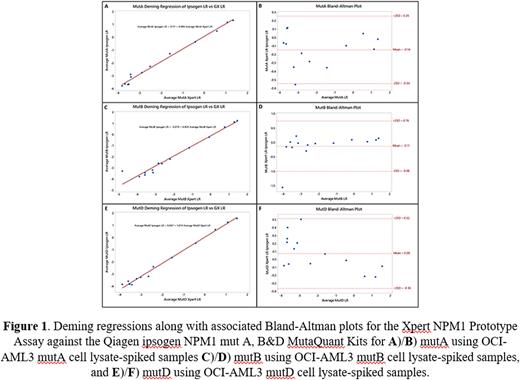
Three NPM1-positive cell lines, OCI-AML3 MutA, OCI-AML3 MutB, and OCI-AML3 MutD, which express NPM1 MutA, NPM1 Mut B, and NPM1 Mut D, respectively, were grown and isolated. After processing the cells into cell lysate, the cell-lysates were spiked into NPM1-negative EDTA whole blood lysate and serially diluted to target 13 or 14 NPM1/ABL levels from approximately 2500% (log reduction (LR) 1.4) to approximately 0.01% (LR -4.0). A subset of each level underwent hands-off sample preparation, total RNA extraction, and RT-qPCR all within the Cepheid GeneXpert automated cartridge system, and another subset had total RNA extracted using the Zymo Direct-zol™ RNA Miniprep Plus Kit. RNA was qualified and quantified using the Thermo Scientific NanoDrop™ 2000 Spectrophotometer before being tested per the comparator assay vendor's recommendations. The Cepheid Prototype assay utilized 4.5mL of lysate, whereas the Qiagen kits used 100 ng of RNA per test. Specimens spiked with cell lines expressing different NPM1 mutations were tested using the respective ipsogen kit designed for that mutation.
The Cepheid Prototype assay was evaluated against the comparator assay for each subtype using Deming regressions. Bland-Altman plots were utilized to evaluate bias between assay quantitation outputs.
Results
Deming regressions and associated Bland-Altman plots showed a high degree of correlation and agreement between comparator assays and the Cepheid Prototype assay (Figure 1).
Conclusions
The novel Cepheid Prototype assay showed a high level of agreement with Qiagen kits in this study using whole blood EDTA lysate samples spiked with three NPM1-positive cell-lysates. Agreement tended to decline at low input levels, and a small but acceptable degree of nonlinearity was present in MutA and MutD. Total time to result (TTR) was minimized in the Cepheid Prototype assay to under 170 minutes, while the comparator assay had a TTR of approximately six hours plus RNA extraction. While RNA extraction is performed within Cepheid Prototype assay cartridge and is included in this 170-minute TTR, the Qiagen kit requires additional expensive and labor-intensive extraction steps that can last one-hour to multiple days, which are not included in the six-hour TTR estimate.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal